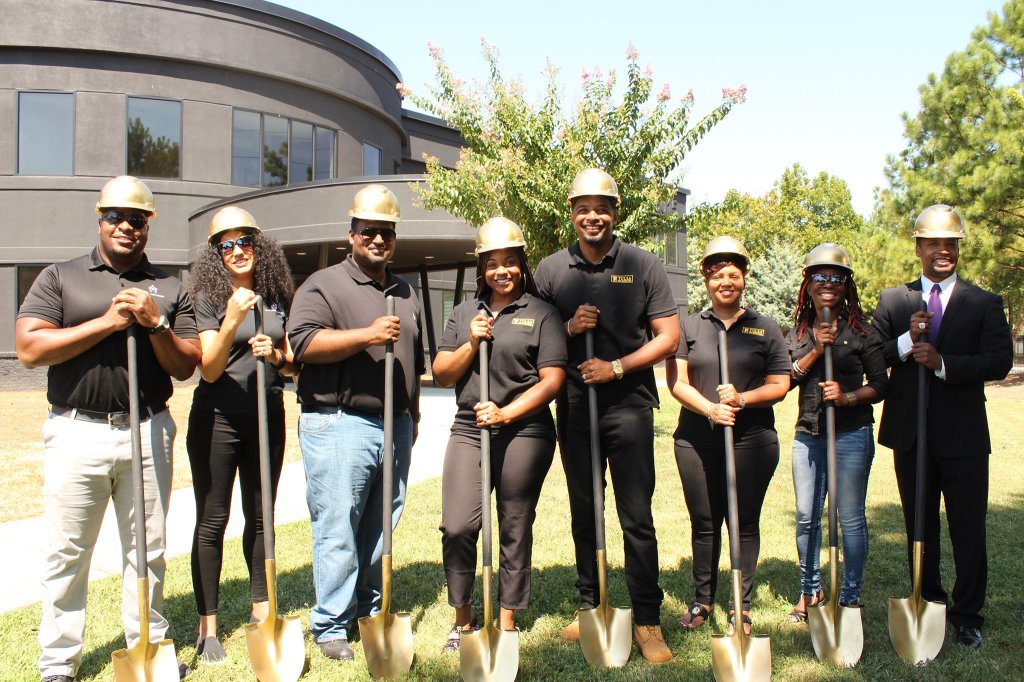
Tulsa Real Estate Fund
Investment Opportunities for All
Did you know that about 90% of millionaires built their wealth through real estate? Between 1932-2012, however, the average American faced multiple barriers to entry for real estate investment. New laws limited participation in investments, placing a hurdle between small-time investors and wealth. Crowdfunding, legalized in 2012, is a relatively new opportunity for people with […]